32 Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells. Made first observation of cells cork C Theodor Schwann 1830s.

A Typical Animal Cell Diagram Cell Organelles Organelles Animal Cell Organelles
This consists of two layers.
. Start studying Table 43- Animal Cell Structure. 34 The Cell Membrane. 43 Plant tissues Next 45 Applications of indigenous knowledge and biotechnology Subsections 1 Epithelial tissue 2 Muscle tissue 3 Nervous tissue 4 Connective tissue 5 Blood 44 Animal tissues ESG6H Tissues are groups of similar cells that perform a particular function.
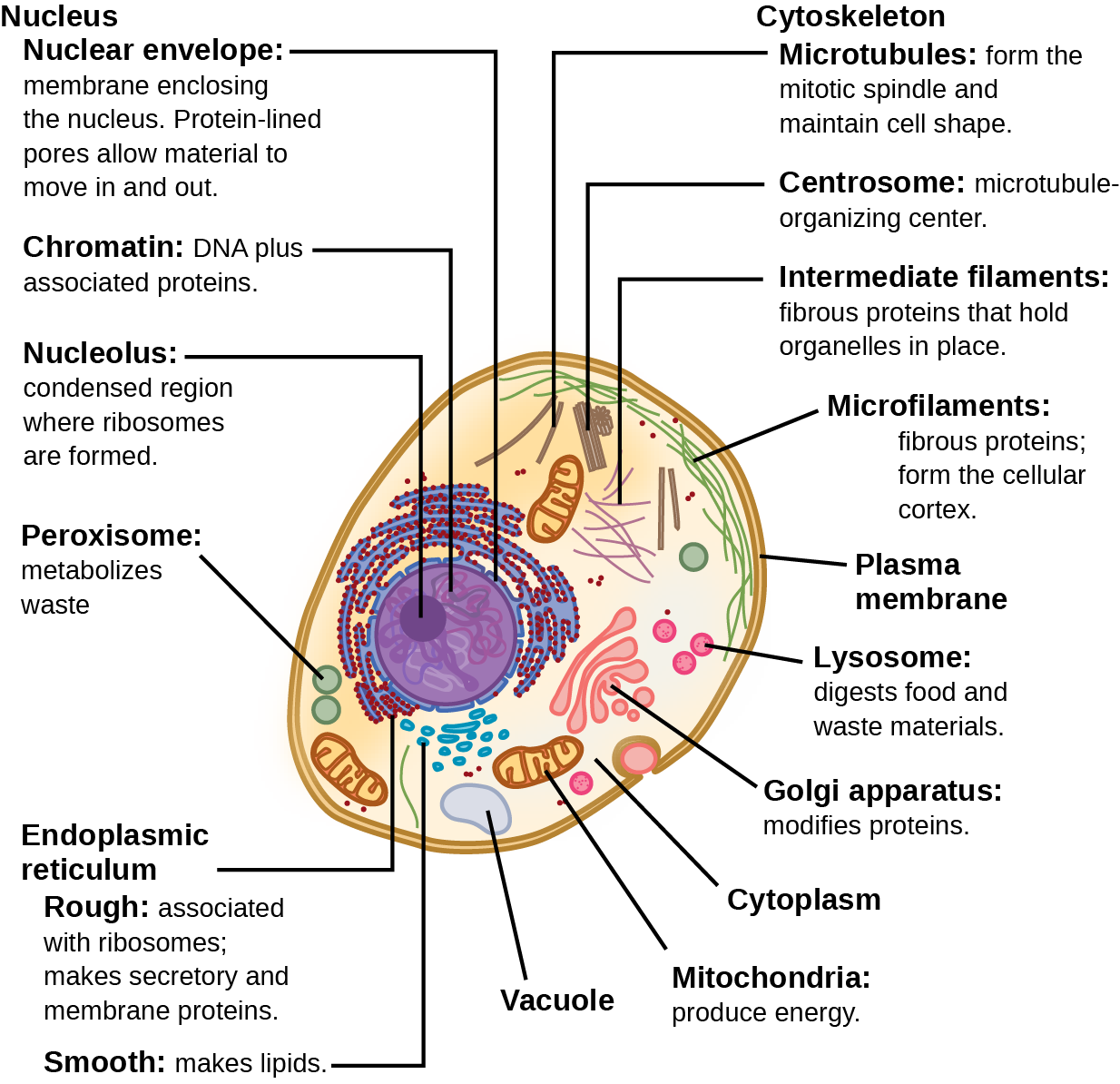
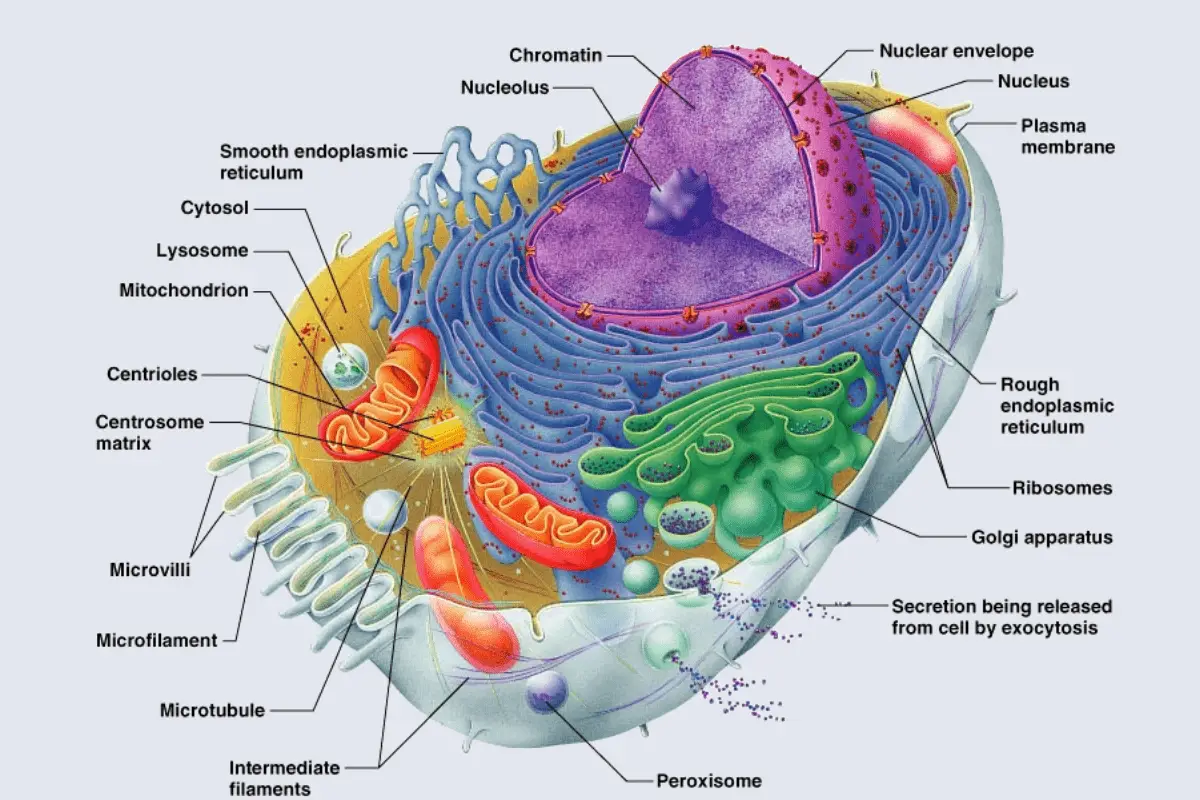
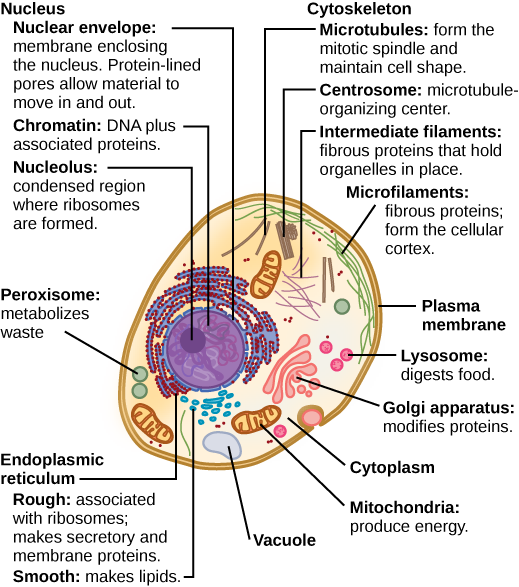
121 Structure Figure 1. Structures you need to know are the cell wall cell membrane cytoplasm plasmids ribosomes flagella nucleus nuclear envelope nucleolus chromatin ribosomes endoplasmic reticulum microtubules microfilaments vacuoles mitochondria Golgi apparatus chloroplasts lysosomes and cilia. Generally vacuoles are.
Introduction to Cell Structure and Function. Basic Form and Function. Figure 48 These figures show the major organelles and other cell components of a a typical animal cell and b a typical eukaryotic plant cell.
Introduction to the Immune System and Disease. Cell Structure and Function The Cell is the Basic Unit of Life Early History. Animal Structure and Function includes the following chapters.
Introduction to the Cellular Basis of Inheritance. Figure 43Diagrammatic sectional view of. It is a living membrane outermost in animal cells but internal to cell wall in plant cells.
Desmosomes tight and gap junctions. All cells come from cells that already exist. Animal cells are linked toge ther by one of three junctions.
Controls what enters and leaves the cell. 31 How Cells Are Studied. Diagram illustrating the structure of a lipid bilayer All cell membranes have as their basic structure a lipid bilayer.
Each cell is composed only of products that it manufactures. Structure and Function Adaptations Unit. Figure 43 STUDY Learn Flashcards Write Spell Test PLAY Match Gravity Created by H_Min9 Terms in this set 8 macrophage engulf bacteria and cellular debris by phagocytosis ground substance component of connective tissue between cells and fibers reticular fiber.
B This scanning electron microscope micrograph shows Salmonella bacteria in red invading human cells yellow. We will be examining human tissues as an example of animal tissues. No cell wall outermost structure is cell membrane or plasma membrane 2.
Site of aerobic respiration. Site of protein synthesis. Their observations led to the development of the cell theory.
It is flexible and can fold in as in food vacuoles of Amoeba or fold out as in the formation of pseudopodia of Amoeba Animal cell 1. The cell is the smallest unit that retains the characteristics of life. They will also learn about animal adaptations and plant adaptations including behavioral adaptations in animals.
First observed of animal cells Lack of cell wall delayed discovery made viewing difficult 1 Every living organism is made up of 1 or more cells. Refer to Figure 48. Introduction to Animal Reproduction and Development.
Each with its own function. 64 Prokaryotic Cell Division. The three main ideas of the cell theory are.
63 Cancer and the Cell Cycle. A Coelomate b Pseudocoelomate c Acoelomate Those animals in which the developing embryo has a third germinal layer mesoderm in between the ectoderm and endoderm are called triploblasticanimals platyhelminthes to chordates Figure 42b. The Plasma Membrane Like prokaryotes eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane Figure 39 made up of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that separates the internal contents of.
This activity includes both animal and plant cell foldables. Each cell makes its own hereditary material. The plant cell has a cell wall chloroplasts plastids and a central vacuolestructures not found in animal cells.
All living things are made of one or more cells. Ad 3B Scientific Supply For Science Medical Patient Education Today. 122 Diagram showing the generalised structure of a plant cell as seen with an electron microscope 1 Calculate the magnification factor.
See answer 1 Best Answer. The students are required to identify and color the organelles on each tab of the foldable using a color key provided. Chemical reactions take place in this jelly-like substance.
All organisms consist of more than one cell. Animal cells have lysosomes and centrosomes. Figure 43 a These Salmonella bacteria appear as tiny purple dots when viewed with a light microscope.
Vacuoles are important membrane. A Robert Hooke 1660s. These foldables are used to teach students the structure and functions of plant and animal cell organelles.
The World of Cells 322CHAPTER 11CellsThe Units of Life. You need to understand the role of the cell membrane. Up to 24 cash back SECTION 4-3 REVIEW CELL ORGANELLES AND FEATURES VOCABULARY REVIEWDistinguish between the terms in each of the following pairs of terms.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Most plant cells do not have lysosomes or centrosomes. Figure 43 Plant cell structure.
Some cellular structures can only be seen. Introduction to the Bodys Systems. Students will learn that animal adaptations and plant adaptations include internal and external structures and that they each structure serves a specific function.
The main subcellular structures in animal cells are. The cell is the basic unit of life in which the activities of life occur. Figure 48 These figures show the major organelles and other cell components of a a typical animal cell and b a typical eukaryotic plant cell.
Mitochondria vacuole nucleus Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi body. What are the cell structures in an animal cell. The plant cell has a cell wall chloroplasts plastids and a central vacuolestructures not found in animal cells.
4Cell Structure Introduction 41Studying Cells 42Prokaryotic Cells 43Eukaryotic Cells 44The Endomembrane System and Proteins 45The Cytoskeleton 46Connections between Cells and Cellular Activities Key Terms Chapter Summary Visual Connection Questions Review Questions Critical Thinking Questions 5Structure and Function of Plasma Membranes. Most plant cells do not have lysosomes or centrosomes.

What Is Life Life Is Knowledge In Action

What Is An Animal Cell Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring And Plant Cell Organelles Cake
Cell Structure And Functions Cell Organelles

Animal Cell Anatomy Diagram Structure All Stock Vector Royalty Free 1012906984 Shutterstock

4 6 Eukaryotic Cells Characteristics Of Eukaryotic Cells Biology Libretexts


0 comments
Post a Comment